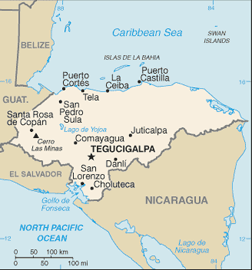
|
|||||||||||
|
CAUTION: The following links
and accompanying text have been culled from the web to illuminate the
situation in Honduras in the early years of the 21st
Century. Some of these links may lead to websites that present
allegations that are unsubstantiated, misleading or even false.
No attempt has been made to validate their authenticity or to verify their
content. HOW TO USE THIS WEBPAGE Students If you are looking
for material to use in a term-paper, you are advised to scan the postings on this
page and others to see which aspects of poverty are of particular interest to
you. You might be interested in
exploring the relationship between distribution of labor and per-capita GDP,
for example. Perhaps your paper could
focus on life expectancy or infant mortality.
Other factors of interest might be unemployment, literacy, access to
basic services, etc. On the other
hand, you might choose to include some of the possible outgrowths of poverty
such as Human Trafficking,
Street Children,
or even Prostitution. There is a lot to the subject of
Poverty. Scan other countries as well
as this one. Draw comparisons between
activity in adjacent countries and/or regions. Meanwhile, check out some of the Term-Paper resources
that are available on-line. Teachers Check out some of
the Resources
for Teachers attached to this website. *** Extreme Weather *** In
Honduras, extreme weather events have become a familiar reality for its
vulnerable communities. Honduras is characterized by its rugged terrain,
dense forests, and coastal lowlands. Unfortunately, these very features make
it highly susceptible to extreme weather events like droughts, heatwaves,
storms, and floods. These events are expected to increase in intensity due to
global heating. Rising sea levels, stronger tides, and more frequent extreme
weather events have become a harsh reality. – adapted from Microsoft BING Copilot World
Bank Climate & Develoment Reports Honduras Country Climate and Development Report, World Bank Group, 16 May 2023 openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/39820 [accessed 11 Dec 2024] Honduras
is highly vulnerable to extreme natural hazards, which are expected to
increase because of climate change. These will have significant consequences
for all of Honduran society, affecting important economic sectors and
threatening food and water security and human health. The impacts of climate
change are expected to disproportionately affect the poorest and most
vulnerable, such as indigenous peoples and afro‑descendants (IPADs) and women. These impacts will likely
compound existing challenges such as migration, internal displacement, and
land conflicts and insecurity. Even though Honduras’s contribution to global
emissions is significantly low, the country has opportunities to pursue low‑carbon development that will
create co‑benefits
and foster synergies with climate change adaptation, particularly in the
agriculture, water, forestry, energy, and transport sector. *** ARCHIVES *** The World Factbook - Honduras U.S. Central Intelligence Agency CIA www.cia.gov/library/publications/resources/the-world-factbook/geos/ho.html [accessed 29
December 2020] World Factbook
website has moved to ---> www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/honduras/ [accessed 5 January 2021] Honduras,
the second poorest country in Central America, suffers from extraordinarily
unequal distribution of income, as well as high underemployment. While
historically dependent on the export of bananas and coffee, Honduras has
diversified its export base to include apparel and automobile wire
harnessing. GDP -
per capita (PPP): $5,600 (2017
est.) Labor
force - by occupation: agriculture:
39.2% industry:
20.9% services: 39.8% (2005 est.) Unemployment
rate: 5.6% (2017
est.) Population
below poverty line: 29.6% (2014
est.) Maternal
mortality rate: 65 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.) Infant
mortality rate: total: 14.6 deaths/1,000 live births Life
expectancy at birth: total population: 74.6 years Drinking
water source: improved: total: 94.8% of
population Physicians
density: 0.31 physicians/1,000 population (2017) Sanitation
facility access: improved: total: 90.2% of
population Electricity
access: electrification - total population: 87.6% (2016) The
Borgen Project - Honduras borgenproject.org/category/honduras/ [accessed 6 February 2021] The Borgen Project works with U.S. leaders to utilize the
United States’ platform behind efforts toward improving living conditions for
the world’s poor. It is an innovative,
national campaign that is working to make poverty a focus of U.S. foreign
policy. It believes that leaders of
the most powerful nation on earth should be doing more to address global
poverty. From ending segregation to providing women with the right to vote,
nearly every wrong ever righted in history was achieved through advocacy. The
Borgen Project addresses the big picture, operating
at the political level advancing policies and programs that improve living
conditions for those living on less than $1 per day. ~
Addressing Child Poverty In Honduras borgenproject.org/child-poverty-in-honduras/ ~
Child Homelessness In Honduras borgenproject.org/child-homelessness-in-honduras/ ~
A Nonprofit To Know: The Work Of Global Pearls borgenproject.org/the-work-of-global-pearls/ ~
Homelessness In Honduras On The Rise borgenproject.org/homelessness-in-honduras/ Uninhabitable:
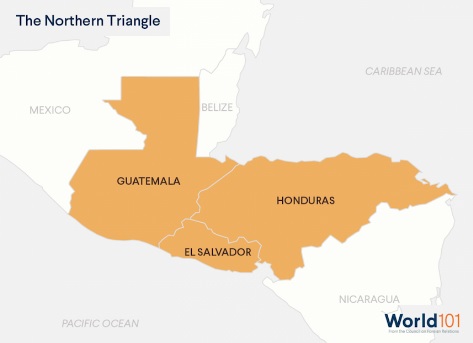
Central America’s Northern Triangle And Beyond Larry J. Schweiger, Pittsburgh Current, 19 March 2021 www.pittsburghcurrent.com/uninhabitable-central-americas-northern-triangle-and-beyond/ [accessed 20 March 2021] Just as
the Irish did during the potato famine, Central American parents are doing
the hard thing out of fear. Facing systemic corruption, hopelessly struggling
in an increasingly hostile climate with deadly gangs, these parents are
sending offspring on a dangerous journey to America. Homeland Security
Secretary Alejandro N. Mayorkas summarized
conditions: “Poverty, high levels of violence, and
corruption in Mexico and the Northern Triangle countries have propelled
migration to our southwest border for years. The adverse conditions have
continued to deteriorate. Two damaging hurricanes that hit Honduras and swept
through the region made the living conditions there even worse, causing more
children and families to flee.
The World Bank in Honduras www.worldbank.org/en/country/honduras/overview [accessed 19 April 2021] During
recent years, Honduras has registered the second highest economic growth
rates in Central America, only behind Panama and well above the average in
Latin America and the Caribbean. However, the country faces high levels of
poverty and inequality. Looking
back a few years Advameg, Inc., Encyclopedia of the Nations www.nationsencyclopedia.com/Americas/Honduras-ECONOMY.html [accessed 29 December 2020] Honduras
is one of the poorest and least developed countries in Latin America. The
economy has been based mostly on agriculture, and over a third of the labor force in 2001 were still involved in this sector. However,
agriculture's contribution to the overall GDP fell from 27% in 1998 to 18% in
2000 mainly due to the damage done to export crops by Hurricane Mitch in
October 1998. About 16% of the land is arable, located mostly along the
coastal plains. Coffee and bananas account for 65% of total Honduran export
revenues. The vast majority of banana holdings are controlled by two US
companies, United Brands and Standard Fruit, and most other profitable
agricultural enterprises are owned by a small number of private citizens. All
material used herein reproduced under the fair use exception of 17 USC § 107
for noncommercial, nonprofit, and educational use. PLEASE RESPECT
COPYRIGHTS OF COMPONENT ARTICLES. Cite this webpage as: Prof. Martin
Patt, "Poverty - Honduras", http://gvnet.com/poverty/Honduras.htm,
[accessed <date>] |